Risk assessment is a critical process that helps organizations identify potential hazards and implement measures to control them. In this article, we will discuss how to prepare risk assessment and cover all elements related to work permit risk assessment.
Definitions
Risk assessment
All activities have an element of risk that has to be managed. In refinery operation and maintenance, the risks are many, high in both probability and consequences, unless adequately managed. Managing these risks by adopting and employing work permit risk Assessment methods are therefore the essence of controlling loss. This can be done by following steps:
- Identify the hazard.
- Assess the risk
- Put controls/safe guards in place
- Re-assess the risk with control in place.
- Confirmation of reduced risk.
Hazard
A condition with a potential for accidental loss.
Risk
A measure of how likely and how serious an incident can be. It comprises of two Components.
- Likelihood – What are the chances of it happening?
- Severity- If it did happen how bad would it be?
Who will prepare A Risk Assessment?
People who control or carry out onsite jobs, and use work permits to do so are the People who should conduct work permit risk assessment. They shall be thoroughly and formally trained in all aspects of work permit risk assessment and be able to demonstrate full understanding and practical application; in other words they shall be made competent.
- Team led by Area section head/senior engineer.
- Area safety engineer
- Concern job engineer.
- Shift supervisor and any other engineer if necessary.
When Risk Assessment To Be Prepare
Work Permit Risk Assessments shall be done for all critical jobs. It shall be done before the job is started.
How To Prepare Risk Assessment
1. Identify the Job and Hazards
The first step in doing a risk assessment is to identify the job and hazards associated with it. This involves understanding the task or activity, identifying the potential hazards, and assessing the likelihood of harm or damage occurring.
For example, if the job is to clean a roof, the hazards associated with it may include falling from height, exposure to chemicals or hazardous substances, and risk of electrical shock.
2. Assess Likelihood and Severity
The next step is to assess the likelihood and severity of the potential hazards. Likelihood refers to the probability of the hazard occurring, while severity refers to the extent of harm or damage that could result.
Likelihood and severity are typically assessed on a scale of 1 to 4, with 1 being the lowest and 4 being the highest. The likelihood and severity scores are then multiplied to determine the overall risk level.
For example, if the likelihood of falling from the roof is rated as 4 and the severity of the resulting injury is rated as 4, then the overall risk level would be 16 (4 x 4 = 16).
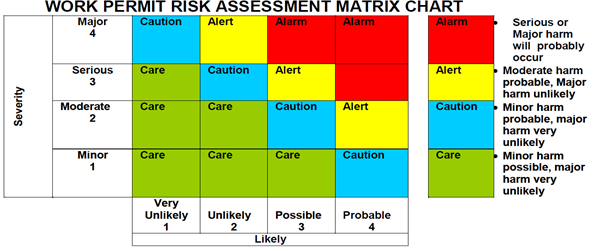
3. Use the Matrix Chart to Determine Risk Level
The risk level is determined by using a matrix chart that plots the likelihood and severity scores on a graph. The likelihood of occurrence is given horizontally at the bottom, and the severity of the consequences is given vertically on the side.
The block where the likelihood and severity scores meet is the risk level. The risk levels are graded in the chart and colored red, yellow, blue, and green in the order of reducing severity.
For example, if the risk level is 16 (as determined in step 2), it would fall in the red zone, indicating that it poses a significant risk and requires immediate action.
4. Take Measures to Reduce Risk
The purpose of the risk assessment is to identify potential hazards and take measures to eliminate or reduce them to an acceptable level. This can be done by employing controls or safeguards, doing the job in different ways, or deciding not to do the job at all if an acceptable level of risk cannot be achieved.
For example, if the risk level of falling from the roof is too high, measures can be taken to reduce the risk, such as using fall protection equipment, providing training on safe work practices, or assigning the job to a qualified professional.
5. Reassess and the Risk
Once measures have been taken to reduce the risk, the risk assessment should be reassessed to determine if the risk level has been reduced to an acceptable level. If the risk level has been reduced to a level that is acceptable, the risk assessment is completed, and the job can proceed.
It is essential to document the risk assessment and retain it for future use. If the same job is being done again, the risk assessment should be reviewed to ensure that it is still relevant and that nothing has changed.
6. Apply the Appropriate Actions
Depending on the risk level, take appropriate action to control or eliminate the hazard. The actions to be taken at each level are:
-
CARE: If the risk level is in the green zone, the hazard is low risk, and no further action is needed.
-
CAUTION: If the risk level is in the blue zone, the hazard is moderate risk, and additional control measures are needed to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
-
ALERT: If the risk level is in the yellow zone, the hazard is high risk, and the activity must be stopped immediately. The supervisor must be informed, and additional control measures must be implemented to reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
-
ALARM: If the risk level is in the red zone, the hazard is very high risk, and the activity must be stopped immediately. The supervisor must be informed, and a full reassessment of the hazard must be conducted to determine how the risk can be reduced to an acceptable level.
7. Documenting the Risk Assessment
It is essential to document the risk assessment process and keep it for future reference. The risk assessment documentation should include the hazard identified, the likelihood and severity assessed, the risk level determined, and the control measures implemented. The documentation should also be reviewed regularly to ensure that it remains up to date and relevant.
Conclusion
A risk assessment is an essential process for identifying potential hazards and assessing the risks associated with them. It is a critical component of health and safety management in workplaces and can help prevent accidents, injuries, and illnesses. By using a risk matrix chart, you can easily identify the risk level associated with a hazard and take appropriate action to control or eliminate the hazard. It is important to document the risk assessment process and regularly review it to ensure that the control measures are effective and the risk level remains acceptable.
In addition to the steps outlined above, there are a few other things to keep in mind when conducting a risk assessment:
-
Involve employees: It is important to involve employees in the risk assessment process, as they are often the ones who are most familiar with the hazards in their workplace. By involving employees, you can get a better understanding of the hazards and potential risks associated with them.
-
Consider the environment: When assessing risks, it is important to consider the environment in which the activity is taking place. Factors such as weather conditions, lighting, and noise can all affect the likelihood and severity of a hazard.
-
Use a variety of methods: There are many different methods that can be used to assess risks, including checklists, brainstorming sessions, and expert analysis. It is important to use a variety of methods to ensure that all potential hazards are identified.
-
Prioritize risks: Not all risks are created equal. It is important to prioritize risks based on their likelihood and severity, so that you can focus your efforts on the most significant hazards.
By following these tips and using a risk matrix chart, you can effectively assess risks and take appropriate action to control or eliminate hazards in your workplace. Remember, a risk assessment is not a one-time event, but an ongoing process that must be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure the safety of everyone involved.



