Scaffolding is an essential tool for construction and maintenance activities that require working at heights. A scaffold is a temporary platform that supports workers, tools, and materials during construction, repair, or maintenance tasks. However, scaffolding can be hazardous if not used properly. In this article, we will discuss the hazards of scaffolding, the precautions required to ensure safety, types of scaffolding, scaffolding components, and work-at-height safety.
What is Scaffolding?
Scaffolding is a temporary structure that is erected to provide a safe working platform for workers to carry out their tasks at heights. Scaffolds are commonly used in construction, maintenance, and repair activities. They are typically made of steel or aluminum and consist of different components that work together to form a safe and secure working platform.
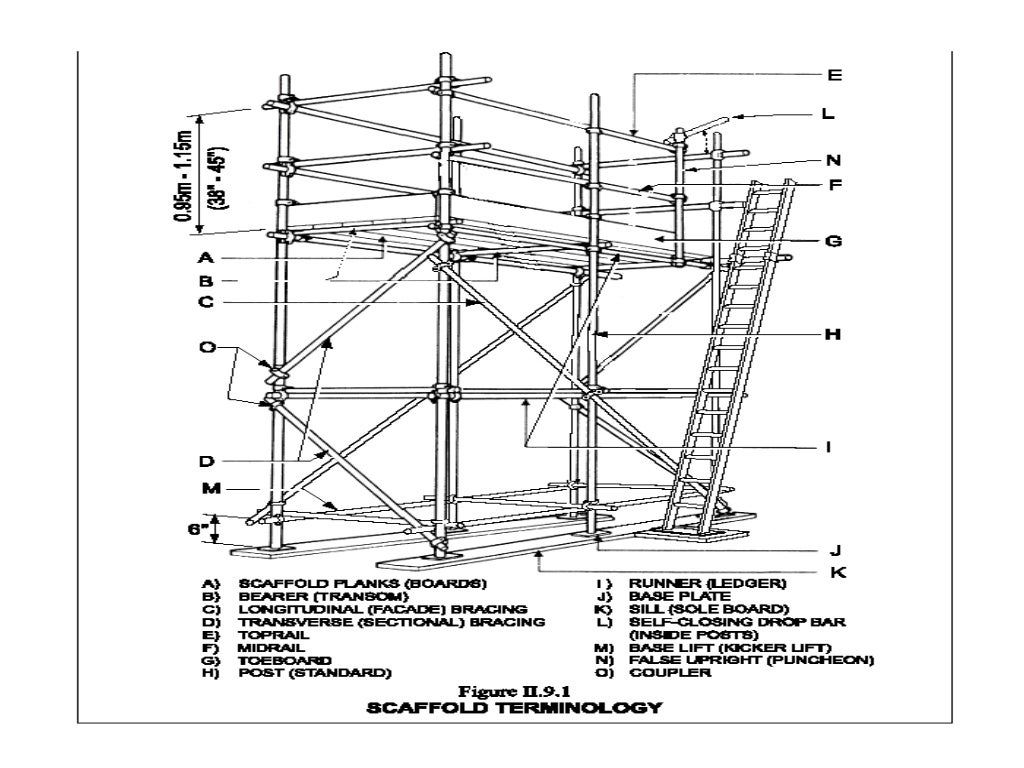
Scaffolding Components
Scaffolding consists of different components that work together to provide a safe and secure working platform. The following are the main components of scaffolding:
- Sole plate – A plate used to distribute the load of the scaffold onto the ground.
- Base plate – A plate that sits on the sole plate and supports the vertical standards of the scaffold.
- Standards – Vertical tubes that support the horizontal ledgers and the working platform.
- Ledgers – Horizontal tubes that connect the standards.
- Bracing – Diagonal tubes that provide stability to the scaffold.
- Decking – The working platform that rests on the ledgers.
- Guard rails (Hand rails and mid-rails) – Rails that prevent workers from falling off the scaffold. They should be at least 1 meter in height.
- Toe board – A board that prevents tools and materials from falling off the scaffold. It should be at least 6 inches in height.
- Clamps – Used to connect the different components of the scaffold. The standard clamps are EN-74 and BS-15.
- Ladder – Provides access to the working platform. It should be secure at three locations.
- Tags – Green or red tags used to indicate the status of the scaffold. They should be renewed after one week.
Hazards of Scaffolding:
Scaffolding is one of the most dangerous activities in construction and can lead to serious injuries or fatalities if not done correctly. The most common hazards associated with scaffolding include:
1. Unsecured ladder slipping:
Workers may slip while climbing a ladder, especially if the ladder is not secured correctly. This can cause serious injuries or even death.
2. Use of unsuitable, damage and faulty materials:
Scaffolding must be constructed using suitable materials and checked regularly to ensure it is in good condition. Faulty or damaged materials can cause the structure to collapse, leading to serious injuries or fatalities.
3. Inadequately supported scaffold boards
Scaffold boards must be properly supported to avoid the risk of collapse. If they are not supported correctly, workers can fall from height, causing serious injuries or fatalities.
4. Omission/removal of guard rails
Guard rails are essential in preventing falls from height. If they are omitted or removed, workers are at risk of falling from the scaffolding.
5. Not proper tie-in/braced
Scaffolding must be properly tied-in and braced to prevent it from toppling over. Failure to do so can cause serious injuries or fatalities.
6. Overloading of platform and board
Overloading of the scaffold platform and boards can cause the structure to collapse, leading to serious injuries or fatalities.
General Safety Precautions for Scaffolding:
1. A competent third-party certified person is allowed for scaffolding job:
It is important to hire a competent person who is certified by a third-party to do scaffolding work. A certified person will have the knowledge and experience to erect and dismantle the scaffold properly, ensuring the safety of workers.
2. Cold work permit is required:
Before starting the scaffolding work, a cold work permit is required. This permit ensures that all necessary precautions are taken to avoid accidents and injuries.
2. Employees shall be used chin straps, leather gloves, and safety harness full time:
Workers working on scaffolding should wear chin straps, leather gloves, and a safety harness at all times. This PPE will protect them in case of a fall.
3. Tools and spanners shall be secured with the body:
Workers should secure their tools and spanners with their body while working on scaffolding. This will prevent tools from falling and causing injury to workers below.
4. Area shall be barricaded, and signboards shall be displayed:
The area where scaffolding work is being done should be barricaded, and signboards should be displayed to warn people of the potential danger.
5. Non-sparking tools shall be used in a hazardous area:
If there is a risk of explosion or fire in the area, workers should use non-sparking tools to prevent accidents.
6. Materials, clamps shall not drop or through:
Materials and clamps used for scaffolding work should not be dropped or thrown from height as they can cause injury to workers or damage to property.
7. Leather bags shall be used for shifting:
Leather bags should be used to shift materials and tools on scaffolding to avoid the risk of dropping them.
8. While erection and modifications, red tag shall be displayed at a height equal to eye level:
A red tag should be displayed at eye level on the scaffolding during erection and modification to indicate that the scaffolding is under construction and should not be used.
9. If height exceeding the ratio, additional tie-in with nearby existing structure shall be given:
If the scaffolding height exceeds the prescribed ratio, additional tie-ins with nearby structures should be provided to ensure stability.
10. Job shall be suspended in case of heavy wind more than 65kmph and rain:
Scaffolding work should be suspended in case of heavy wind or rain as it can be hazardous to workers.
11. Dismantling starts from the top:
Scaffolding dismantling should start from the top and work downwards to prevent accidents.
12. Scaffolding tag shall be renewed after one week, and a checklist shall be maintained:
The scaffolding tag should be renewed every week, and a checklist should be maintained to ensure that all safety measures are being followed.
13. Ladder shall be raised at least one meter above the landing platform and should be secure at three locations:
Ladders used for scaffolding work should be raised at least one meter above the landing platform and should be secure at three locations to prevent accidents.
14. Properly train workers:
It’s important to provide proper training to workers before allowing them to work on scaffolding. Workers should be trained to recognize the hazards associated with scaffolding work, including the dangers of falling, the risks associated with using power tools, and the need for proper safety gear.
15. Use safety harnesses
Workers should wear safety harnesses when working on scaffolding, especially when working at heights greater than 1.8 meters. The safety harness should be securely anchored to a suitable point, and workers should be trained to use the harness properly.
16. Keep the workplace clean
Cluttered or poorly maintained work areas can increase the risk of accidents, so it’s important to keep the workplace clean and free of obstacles. Workers should also be trained to recognize the hazards of a cluttered work area and encouraged to maintain a tidy workspace.
17. Loose materials and clamps should not be kept unattended on the working platform.
Loose materials and clamps can fall and cause serious injuries to the workers below. All materials should be secured and properly stored in designated areas.
18. Risk assessment is required if wind speed is more than 50kmph
The scaffolding structure can become unstable and pose a significant risk to workers in case of strong winds. It is important to assess the risk and take necessary measures to ensure safety.
19. Mobile scaffold casters (wheels)
Mobile scaffold casters (wheels) diameter should be 5 inches (12.7cm) and swivel lock required. This will ensure the scaffold remains stable and secure during movement.
20. Gin wheel (pulley and rope)
Gin wheel (pulley and rope) should be used for light material lifting. Heavy materials should be lifted using a hoist or crane. This will prevent strain and injury to workers who are manually lifting materials.


General Safety Precautions for Ladder Safety:
Ladders are essential tools used in construction, maintenance, and other industrial jobs. To ensure safety while using ladders, follow these general safety precautions:
1. Ladder should be of industrial type
Industrial ladders are designed to withstand the rigors of daily use in a workplace environment.
2. Use the right type of ladder for the job:
Different jobs require different types of ladders. Always select the right ladder for the job to ensure safety.
3. Inspect the ladder for defect and damage before use:
Before using a ladder, always inspect it for any defects, cracks, or damages. If any are found, the ladder should not be used until it is repaired.
4. Independent ladder shall be tagged:
Independent ladders should be tagged with the date of inspection and the name of the inspector. The validity of the tag should be for a month.
5. Ladder shall be positioned at 75-degree angle:
Ladders should be positioned at a 75-degree angle from the ground to ensure stability and safety.
6. Ladder shall be secured with clamps at 3 locations:
Ladders should be secured with clamps at three locations to prevent slipping and sliding.
6. Only one person shall climb at a time and face the ladder during up and down:
Only one person should climb the ladder at a time, and they should always face the ladder during ascent and descent.
7. Do not carry tools and materials while climbing
Carrying tools and materials while climbing can cause the ladder to become unbalanced and lead to falls.
8. Metal ladder shall not be used for electrical works:
Metal ladders should not be used for electrical work as they conduct electricity and can cause electrocution.
Note: Please be aware that the ratios, mathematical numbers, types, and other rules mentioned in this article are in accordance with the guidelines set by KNPC. However, it is important to note that these may vary from client to client, and it is advisable to always check and follow the specific guidelines and regulations of your organization or client before proceeding with any scaffolding or work at height activities.
Types of Scaffolding
There are different types of scaffolding, and each type is used based on the construction needs and job requirements. Here are the most common types of scaffolding:
1. Independent Tied Scaffolding:
This type of scaffolding is built independently and tied to a building or structure for stability. The independent tied scaffolding is further categorized into light-duty, medium-duty, and heavy-duty scaffolding based on the weight it can hold.
2. Stationary Scaffolding:
Stationary scaffolding is fixed to the ground and used for construction work that does not require mobility. The height of the stationary scaffolding shall not exceed 18.3 meters (60 feet) and shall not exceed four times the minimum base ratio.
3. Mobile Scaffolding:
Mobile scaffolding is a type of scaffolding that can be moved from one place to another. The height of the mobile scaffold shall not exceed 12.2 meters (40 feet), and the ratio should be 1:3 (1 base and 3 height). It consists of castor wheels and a single working platform. The caster wheel shall be a minimum of 12.7 cm (5-inch) diameter with rubber types and should be locked while using.
4. Cantilever/Suspended Scaffolding:
This type of scaffolding is used when it is impractical or impossible to erect a standard scaffold on the ground or other surfaces. Rakers (bottom diagonal one for every standard) shall be used, and the angle of rackers shall not be greater than 35 degrees.
Ratios of Scaffolding
It is essential to use the correct ratio of scaffolding to ensure that it is safe and stable. Here are the ratios for mobile and tower scaffolding:
- Mobile Scaffold: The ratio of mobile scaffold should be 1:3, which means one base for every three heights. It should not exceed 12.2 meters (40 feet) and must consist of caster wheels and a single working platform. The caster wheels should be at least 12.7 cm (5 inches) in diameter, made of rubber, and have locks.
- Tower Scaffold: The ratio of tower scaffold should be 1:4, which means one base for every four heights. The height should not exceed 18.3 meters (60 feet), and it should not exceed four times the minimum base ratio.
Best Practices for Working at Height
Working at height can be dangerous, so it is essential to follow best practices to prevent falls and other hazards. Here are some tips for working at height:
- Keep the workplace free of obstacles and clutter.
- Keep the walking surface clean and dry.
- Block or barricade the area while cleaning floors.
- Clean up spills immediately or barricade the area.
- Report hazards on the surface immediately.
- Avoid running cables or cords on the walkways.
- Use ladders safely.
- Ensure scaffolds are erected by a competent person and follow a tagging system.
- Wear proper footwear.
- Maintain adequate illumination.
- Do not jump from an elevated surface.
- Floor openings should be covered and barricaded.
- Do not engage in horseplay.
- Use a safety harness if working at height (more than 1.8 meters).


Hi there it’s me, I am also visiting this web
site on a regular basis, this website is genuinely nice and
the people are actually sharing good thoughts.
Hi thanks alot for the deep detailed lactures abt scaffolding
A very detailed and useful information about scaffolds. I have learnt a lot
Appreciated
This is a very good detailed information about scaffolding safety. Scaffolding safety depends on its preparation
Scaffolding safety is absolutely critical on any construction site. As a general contractor, I appreciate the emphasis on proper training, inspection, and maintenance. The risks associated with scaffolding are significant, and staying vigilant with safety protocols can prevent costly accidents. In particular, ensuring that scaffolding is set up correctly for projects involving intricate work like stucco application can make all the difference. What additional safety measures do you recommend for contractors working on multi-story scaffolding in challenging weather conditions?